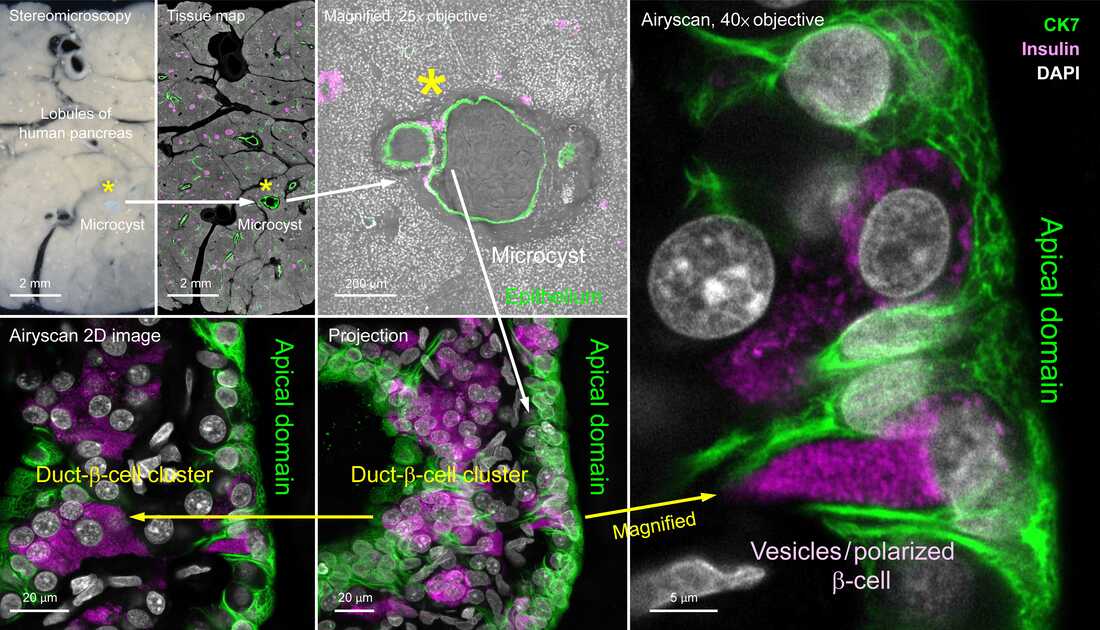
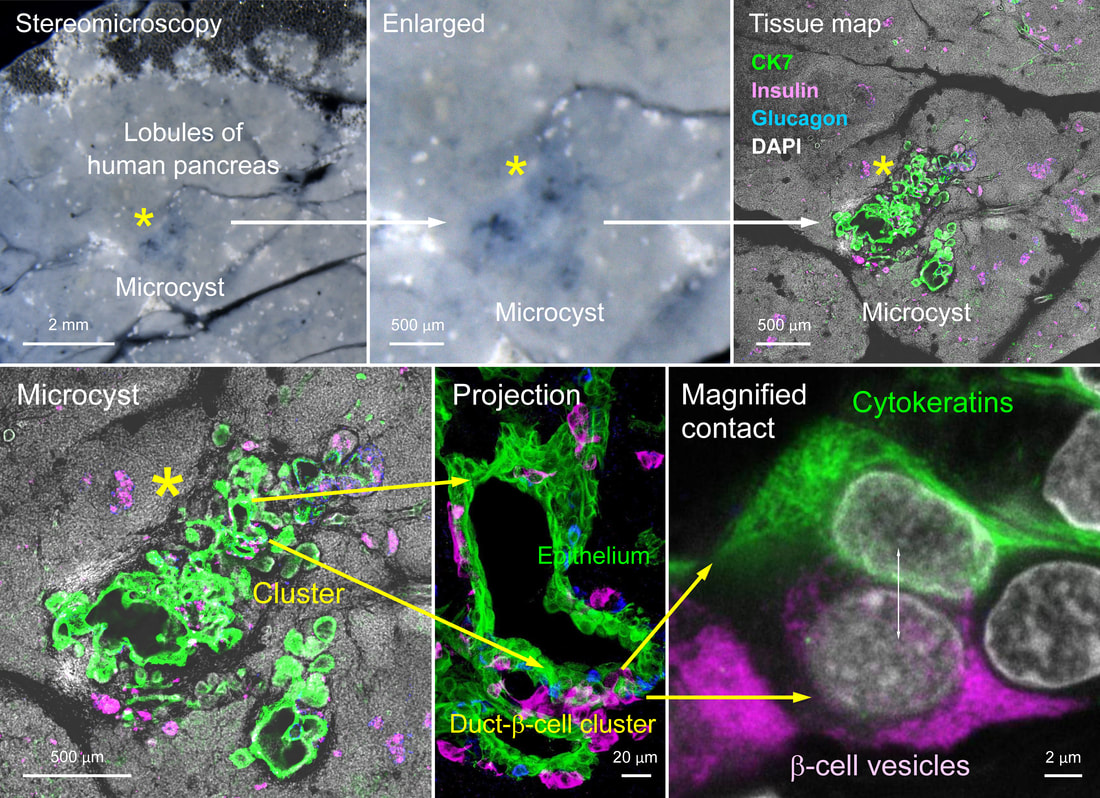
Human pancreatic microcyst and duct-β-cell cluster (2025)
|
|
|
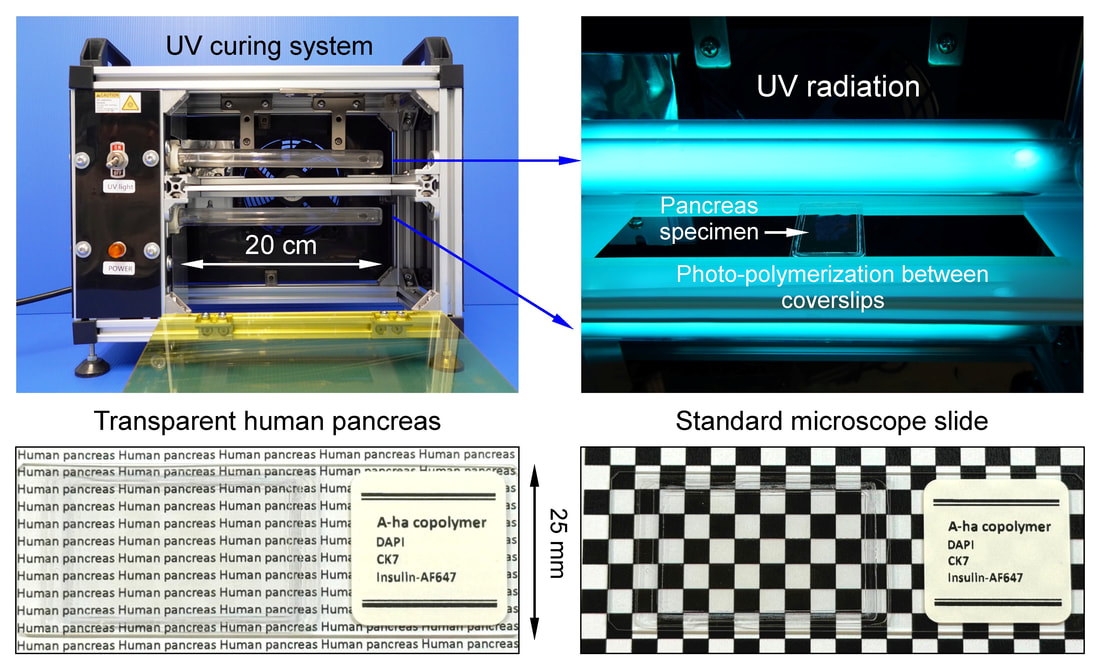
==== Antifade human pancreas polymerization established in Nat. Commun 2023 ====
Team-based human pancreas analysis in Taiwan (2022)
In the past five years, we has successfully transformed our 3-D imaging platform from mouse to human pancreas characterization. We integrate the fields of surgery, pathology, and modern 3-D histology to investigate the human pancreas in health and disease. Our ongoing work includes: (i) use of organ-wide PanIN and microadenoma analyses to elucidate exocrine-endocrine relationship in early pancreas remodeling and (ii) use of modern 3-D histology (integration of vibratome and microtome histology) to establish an image database of early lesions in the human pancreas.
Low-grade duct lesion (PanIN) in human donor pancreas (2022)
Associated human islet and duct remodeling (2022)
Article: Local islet remodelling associated with duct lesion–islet complex in adult human pancreas (2021 Diabetologia)
Review: Pancreas optical clearing and 3-D microscopy in health and diabetes (2021 Frontiers in Endocrinology)
Human pancreatic fatty infiltration. Images were derived from tile scanning of optically cleared pancreatic specimens. (A-B) Normal lobule of human pancreas. Adipocytes are clearly seen around the blood vessel and inside the lobule (magnified, arrows). Green, nuclear staining; red, CD31. (C-D) Acinar atrophy of diseased lobule. This view was acquired 2-cm distal to the pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Overlay of transmitted light and fluorescence signals identifies the fatty infiltration.
Article: Autonomic innervation of human pancreas (2019 AJP-GI)
Article: Lymphatic vessel remodeling and invasion in pancreatic cancer progression (2019 EBioMedicine - The Lancet)
Association of PanIN and lymphatic network in surgical biopsy acquired from PDAC treatment. The H&E image in inset i shows high-grade PanIN in the tumor bulk (male/age, 67 years/T3N0). 2-D fluorescence image (inset ii) and 3-D projection of signals (inset iii) identify the peri-PanIN lymphatic network. Blue: islets (glucagon staining). Green: nuclei. Yellow arrows indicate the areas with aggregation of nuclear signals (inflammation), which appear to be associated with the lymphatic network (magenta, D2-40).
3-D multiplex histology of human pancreas (2020 DDW abstract)
Integration of transmitted light, fluorescence, and H&E signals to identify neuro-insular network in PanIN microenvironment. A PanIN lesion was detected in the vibratome section of human pancreas (circle, A) and confirmed with the microtome-based H&E histology (B, gold standard). The peri-lesional adipocyte association (transmitted light signals), islet aggregation (yellow, glucagon staining), and neuro-insular association (white in C & D, PGP9.5) are revealed via 3-D imaging with tissue clearing.
Islet aggregation around early duct lesions in human donor pancreas (American Diabetes Association 2019 Scientific Sessions)
Islet aggregation around early duct lesions in human donor pancreas (American Diabetes Association 2019 Scientific Sessions)
Human pancreatic neuro-insular network in health and fatty infiltration (2018 Diabetologia)
Panoramic view of pancreatic glial network and intra-pancreatic ganglia. Cyan: S100B. Red: CD31. Yellow: nuclei. This video shows a peri-lobular ganglion at the beginning (00:00-00:06, left side of the image stack), then the view moves to an islet and its nearby intra-parenchymal ganglion (00:09-00:12). Dimension: 3,600×2,100×300 μm.
Human pancreatic neuro-insular network (American Diabetes Association 2017 Scientific Sessions)